Nampons™ are clinically proven to stop nosebleeds fast
Nampons contain a proprietary and patented active micro-dispersed oxidized cellulose that stops anterior bleeding fast. Oxidized cellulose has been used for over 50 years by millions of hospitals and first responders to help stop mild to moderate bleeding.
Efficacy
In 2017, a comprehensive study of nasal plugs impregnated with oxidized cellulose was performed over a two-year period and published in the Netherlands by Dr. teGrotenhuis. The paper, titled "Use of Hemostatic Nasal Plugs in Emergency Medical Services In The Netherlands," concluded that the nasal plugs are an effective adjunct in the prehospital treatment of severe and uncontrolled epistaxis (nosebleeds).
Furthermore, initial clinical studies performed in 1999-2000 in the Czech Republic examined the hemostatic power of oxidized cellulose in surgical applications. This multicenter, randomized trial involved>200 patients. A number of different surgical procedures were used for this evaluation, including maxillofacial surgery, general abdominal surgery, thoracic surgery, pulmonary surgery, and Aesthetic surgery. This trial randomly divided all patients into two groups: one with sterile, oxidized cellulose powder applied to control bleeding in half the patients, using normal surgical bleeding procedures; and the control group, which used only normal surgical bleeding procedures. As expected, from a safety perspective, no adverse events were reported. A significant reduction in bleeding (p<0.001) was observed when oxidized cellulose was used.
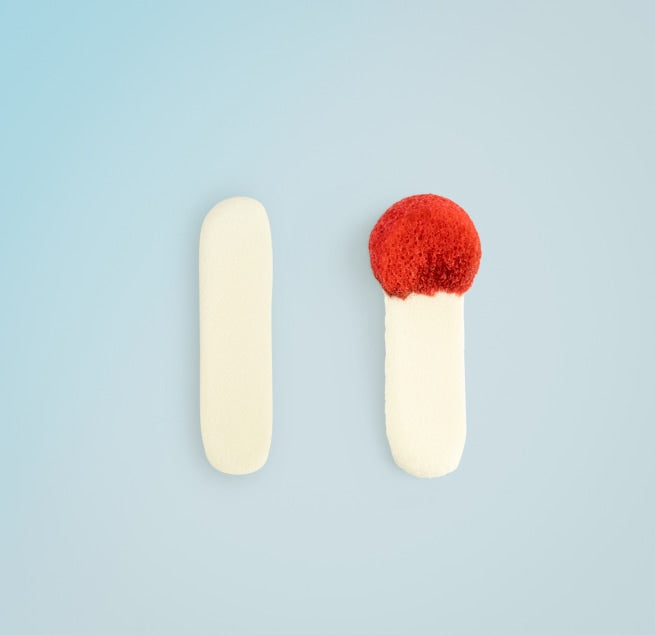

How Nampons™ stop the bleed
When applied to a wound, it produces several effects. First, the oxidized cellulose in Nampons® physically retards blood flow, slowing the bleed. In addition, the SMOC™ technology in Nampons™ provides a surface or scaffold for proteins and cells in the blood to bind to and interact with, thereby promoting faster blood clotting.
Secondly, SMOC™ absorbs water and swells to form a gel-like structure. This, combined with the binding of large proteins and cells in the blood, effectively creates a "plug" that acts as a physical barrier to bleeding.
Lastly, SMOC™ activates platelets in the blood. These activated platelets aggregate, significantly reducing blood clotting time and thereby stopping the bleeding.
Publications
- “The influence of intrinsic coagulation pathway on blood platelets activation by oxidized cellulose.” J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007 Aug;82(2):274-80. Krízová P, Másová L, Suttnar J, Salaj P, Dyr JE, Homola J, Pecka M.
- “Hemostyptic effect of oxidized cellulose on blood platelets.” Sb Lek. 2003;104(2):231-6.Masova L, Rysava J, Krizova P, Suttnar J, Salaj P, Dyr JE, Homola J, Dostalek J, Myska K, Pecka M.
- “Surface interactions of oxidized cellulose with fibrin(ogen) and blood platelets.” Sensors and Actuators B 90 (2003) 243–249. J. Rysˇava ́a, J.E. Dyra, J. Homolab, J. Dosta ́lekb, P. Krˇı ́zˇova ́a, L. Ma ́sˇova ́a, J. Suttnara, J. Briestensky ́c, I. Santarc, K. Mysˇkac, M. Peckad
- “In vitro and in vivo immunomodulatory effects of microdispersed oxidized cellulose. “ Int Immunopharmacol. 2002 Sep;2(10):1429-41. Jelinkova M, Briestensky J, Santar I, Rihova B.
