
Nampons™ and Nampons™ Kids are the leading OTC brand for the treatment of nosebleeds
Nampons™ are poised to transform the outpatient management of nosebleeds by bringing the same technology utilized by medical professionals for over two decades to in-home use.
Nampons™ are made of medical-grade, compressed PVA that rapidly expands on contact with blood to provide gentle pressure on the nasal mucosa while absorbing 12x more blood than cotton products. Upon expansion, the foam will topically deliver micro oxidized cellulose, a hypoallergenic pro-coagulant that facilitates hemostasis.
-
Effective
- Absorbs 12X the volume as standard tissues
- Expands to provide pressure to slow the bleed intranasally
- Oxidized cellulose facilitates clotting
- The non-stick PVA sponge will not bing to clot reducing the risk for reoccurrence
-
Safe & Proven
- Hypoallergenic
- No known contraindications
- FDA registered Class I medical device
- Used by thousands of children and adults since 2021

How It Works
Fast and Easy Nosebleed Treatment
Nampons™ and Nampons™ Kids are delivered in sterile, easy-to-open single-use foil packs, making them ideal for first-aid kits and medical bags.
- Upon incident of a nosebleed, tear open the foil pack and remove one nasal plug. Insert no more than 3/4th of the way into the nasal cavity
- Nampons™ will immediately expand upon contact with blood, providing gentle pressure to slow the bleed. Tilt head forward while applying gentle pressure to the outside of the nose
- Micro-oxidized cellulose will help stop the bleed. Remove and discard. Repeat if necessary.
Oxidized Cellulose
Clinically Proven Clotting Agent
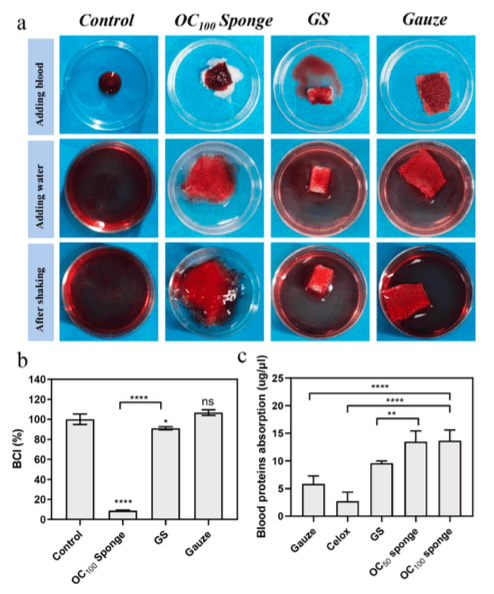
In clinical studies, oxidized cellulose has been proven to be more successful than cotton gauze, commercial gelatin and Celox powder for hemostatic properties. Additionally, studies report that "the OC sponge, due to excellent cytocompatibility as well as antibacterial capacity, could also significantly facilitate wound healing."

Frequently Asked Questions
What age are Nampons™ appropriate for?
Nampons™ Kids are uniquely shaped for children ages 4 - 12 years old, though the size may be comfortable for older children with smaller noses.
Nampons™ are designed for teens, adults and seniors and may be trimmed without a loss of efficacy.
How long should Nampons™ be left in for?
Nampons™ typically stop an anterior bleed within 5-10 minutes and can then be discarded. In some cases, a second Nampon may be required. If the bleed lasts more than 15 minutes or the Nampon™ becomes fully saturated, please advise the patient to seek further medical attention.
Are Nampons™ FSA/HSA eligible?
Yes! Nampons™ are approved by SIGIS for reimbursement submissions under most FSA/HSA plans.
What is the insurance code for Nampons™?
Nampons™ may be covered by insurance under CPT 30901, which covers the use of packing materials to the anterior (front) of the nose for the treatment of epistaxis.
Are there any allergies or counter-indications associated with Nampons™?
Oxidized cellulose, the primary clotting agent in Nampons™ brand products, were developed in the 1950s by the US military for mild-to-moderate wounds. Nampons™ has not received any reports of any counter-indications or adverse effects from the use of our product as a result of using oxidized cellulose for hemostatic properties.
What is Nampons™ FDA registration?
Both Nampons LLC and Nampons™ products are registered with the FDA. Nampons LLC's registration number is 3022627125 and our Nampons™ nasal plugs are listed as Class I medical devices under regulation number 878.4014.

Purchasing, Samples & Patient Coupons
Nampons offers a discount on all medical purchases. For our current price sheet, please email medical@nampons.com.
If you are interested in receiving samples of both Nampons™ and Nampons™ Kids products, as well as patient information brochures and coupons, please click on the button below.
References
"Fabricating Oxidized Cellulose Sponge for Hemorrhage Control and Wound Healing, Shengyu Li, April 18th, 2023 - citation link


